Computed Tomography Scan
What You Need to Know
Home > Blog > Cancer > Cancer Diagnosis > Diagnosis English > CT Scan
This article will be your friendly guide, walking you through what a Computed Tomography Scan is, why it’s used, how to prepare for one, and what to expect. Think of it as a detailed map for your journey into understanding this amazing medical technology.
Summary
- How It Works
- What It's Used For
- What the Procedure Feels Like

Understanding CT Scan
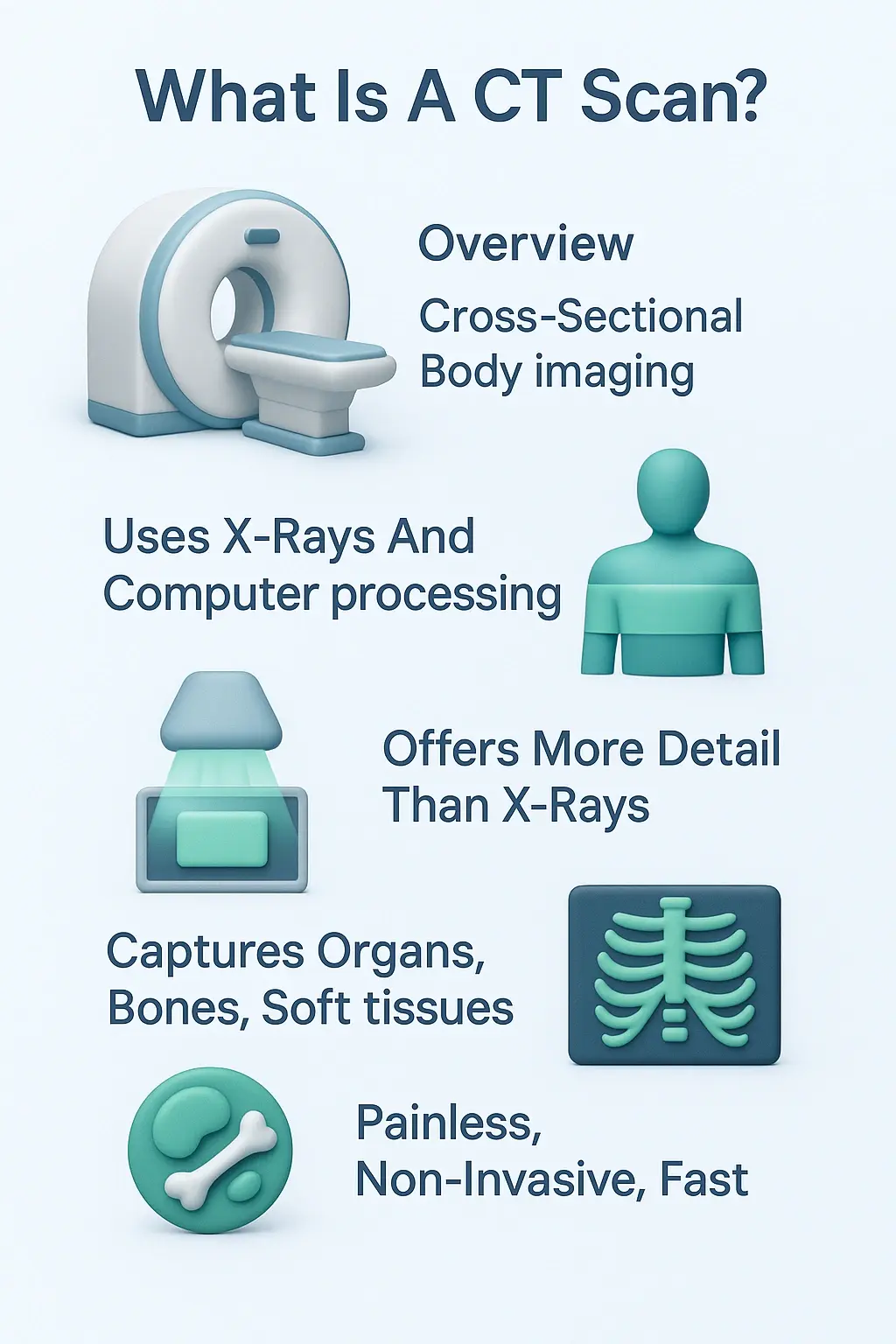
It uses a special X-ray machine that moves around your body in a circle. While it moves, it takes many pictures from different angles. A powerful computer then takes all these pictures and puts them together to create detailed, cross-sectional images, or “slices,” of your body. This allows doctors to see your bones, organs, and blood vessels with great clarity.
A computed tomography ct scan is a powerful diagnostic tool that combines X-rays with computer technology. In the past, it was also widely known as a computerized axial tomography ct scan, which means the same thing. The main goal of any Computed Tomography Scan is to give doctors a clear inside view without any surgery.
- History
The development of CT scan technology began in the early 1970s. It was invented by British engineer Sir Godfrey Hounsfield and South African physicist Allan Cormack, who were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1979. The first successful clinical CT scan was performed in 1971 on a patient with a brain tumor.
- What happens during a CT scan?
Detectors on the opposite side of the machine measure the amount of X-rays that pass through. You won’t feel a thing! The most you’ll have to do is lie very still, and sometimes the technician might ask you to hold your breath for a few seconds. This is to make sure the pictures are not blurry. The computed tomography working principle is based on how different body tissues absorb these X-rays differently, allowing the computer to create a detailed picture.
- How CT scan creates cross-sectional images
It stacks them up like slices of bread to create a detailed 3D view of the part of your body being examined. This process uses technology similar to a computed tomography x ray but is much more advanced. It allows doctors to look at your body one thin layer at a time, making it easier to spot even very small problems that a regular X-ray might miss.
- CT scan vs MRI vs X-ray
| Feature | CT Scan (Computed Tomography) | MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) | X-ray |
|---|---|---|---|
| How it Works | Uses rotating X-rays and a computer to create cross-sectional images. | Uses strong magnets and radio waves to see inside the body. | Uses a single beam of radiation to create a 2D image. |
| Best For | Emergency situations (trauma, stroke), bone fractures, lung and chest issues, cancer detection. | Detailed images of soft tissues like the brain, spinal cord, ligaments, and muscles. | Checking for broken bones, pneumonia, and dental issues. |
| Scan Time | Very fast, typically takes only a few minutes. | Longer, can take from 30 minutes to over an hour. | Very quick, usually takes less than a minute. |
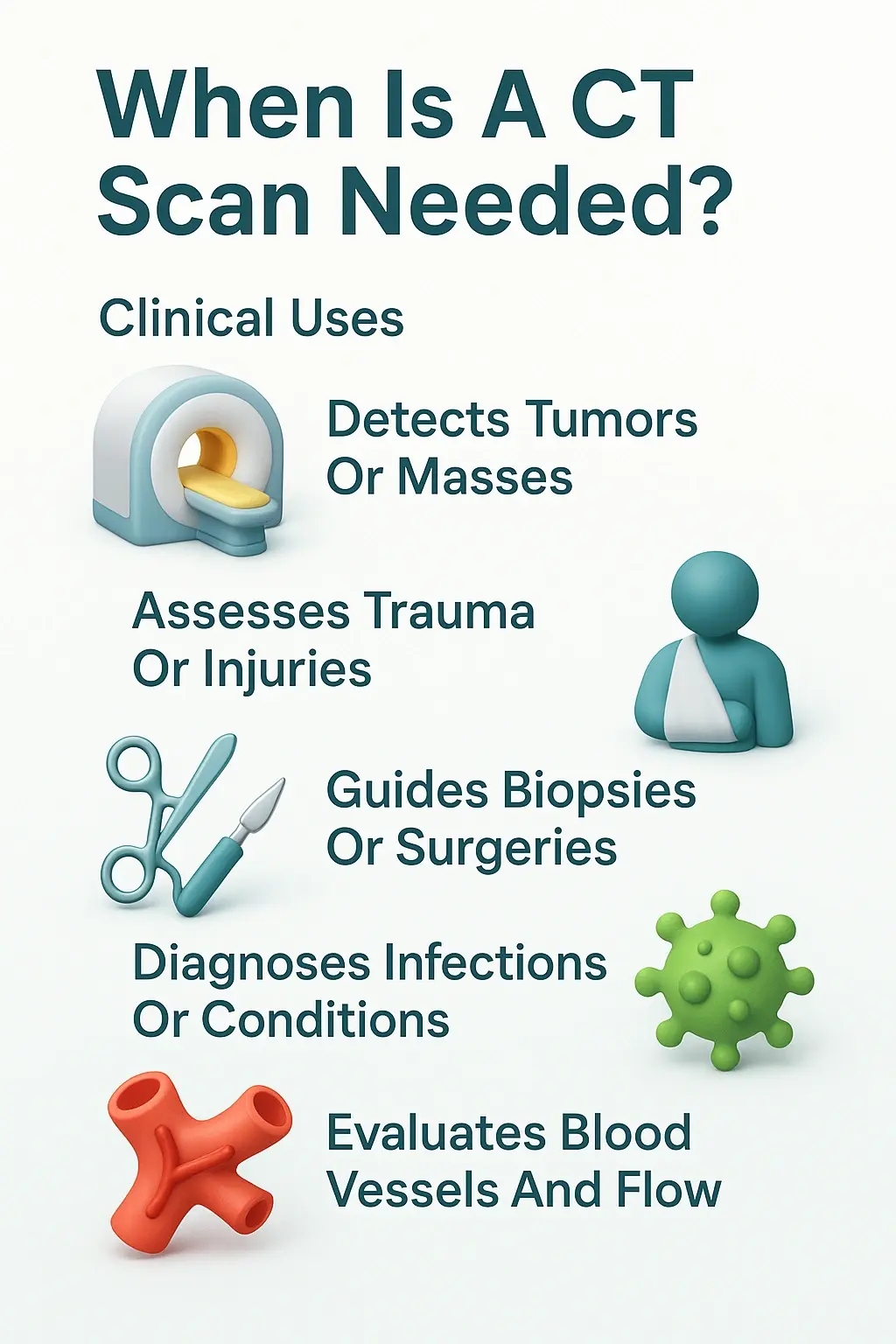
Common Uses of CT Scan
It is one of the most valuable tools in modern medicine for looking inside the human body. Let’s explore some of the most common reasons a doctor might order this scan. If you’ve ever wondered what are ct scans used to find, this section will give you a clear answer.
- Brain and head injury detection
The detailed images help doctors make life-saving decisions quickly. In research, the ct computed tomography scan psychology definition relates to its ability to show brain structures, helping scientists understand how brain abnormalities might affect behaviour.
- Chest and lung disease diagnosis
It can provide much more detail than a standard chest X-ray. Doctors can see the exact size and location of a tumour, which helps them plan for surgery or radiation therapy. It gives a clear picture of the lungs, heart, and major blood vessels in the chest.
- Abdominal and pelvic condition assessment
It’s also used to find tumours in the liver, kidneys, pancreas, or ovaries. For patients who have been in an accident, this scan can quickly identify internal bleeding or organ damage in the abdomen and pelvis, which is critical for immediate treatment.
- Bone fractures and joint problems
It is also useful for examining small bones in the hands and feet or for looking at joints like the shoulder, elbow, or hip in great detail.
Types of CT Scans
Some scans are designed to look at blood vessels, while others are used for general screening. All of them use the same basic technology, but with small changes to get the best possible images for a specific problem. Understanding these types can help you know exactly what kind of scan you are having.
- CT Angiography
It’s used to find problems like blockages, aneurysms (bulges in a blood vessel wall), or other vessel abnormalities. A common example is a cardiac computed tomography ct scan, which is used to look at the arteries of the heart.
- Contrast CT scan
This substance helps highlight specific areas inside your body, making them stand out on the final images. This is very useful for finding tumours or inflammation, as these areas often have a different blood supply than healthy tissue.
- Low-dose CT scan for lungs
It is specifically recommended for long-term smokers or people at high risk of developing lung cancer. It can detect very small nodules in the lungs before they cause any symptoms, which can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment.
- Full body CT scan
Full body CT Scan: A full-body Computed Tomography Scan scans the body from the head to the pelvis. It is not typically used for general health check-ups. Instead, it is most often used in emergency situations, such as after a major car accident, to quickly check for multiple injuries.
It is also used in oncology (cancer treatment) to see if cancer has spread from one part of the body to another (a process called metastasis).
Preparing for a CT Scan

- Food, drink, and fasting guidelines
Fasting is important because it ensures your stomach and intestines are empty, which gives the radiologist a clearer view of your organs. It also reduces the risk of feeling sick if you are given a contrast dye injection. You will usually be allowed to drink clear liquids like water. Always confirm the specific fasting rules for your Computed Tomography Scan.
- Medication adjustments
If you are diabetic and take metformin, you may be asked to stop taking it for a day or two after a CT scan with contrast dye. This is a precaution to protect your kidneys. Your doctor will give you specific instructions.
- What to wear and what to avoid
This includes jewellery, eyeglasses, dentures, hairpins, and clothes with zippers or metal buttons. Metal can interfere with the CT scanner and affect the quality of the images.
| Preparation Step | Why It's Important | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| Fasting | Prevents blurry images of the stomach and reduces the risk of nausea from contrast dye. | Do not eat or drink for 4–6 hours before the scan, as instructed. Water is usually okay. |
| Inform about Health | Helps the medical team ensure your safety, especially regarding allergies or kidney problems. | Tell your doctor about any allergies (especially to iodine), kidney issues, or if you might be pregnant. |
| Clothing & Accessories | Metal can create artefacts (white streaks) on the CT images, hiding important details. | Wear comfortable clothes without metal. Remove all jewellery, piercings, and hearing aids before the scan. |
CT Scan Procedure Explained
Knowing what will happen on the day of your Computed Tomography Scan can help you feel more relaxed. The entire process is managed by a trained professional called a radiologic technologist. They are there to guide you and make sure you are comfortable and safe. The procedure itself is painless and relatively quick. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of what you can expect.

- Arrival and preparation
- Contrast dye use and safety
- Time duration and scanning process
Understanding CT Scan Results
- How radiologists interpret CT images
- When and how results are shared
- Need for further tests or follow-ups
Role of a CT Scan in Cancer Detection and Treatment Planning
- CT Scan for Early Detection and Localization of Tumors
- Importance of CT in Cancer Staging and Surgical Planning
- Advances in CT Imaging for Oncology
Benefits of CT Scanning
- Fast and accurate diagnosis
- Wide body coverage
- Image clarity and 3D reconstruction
Risks and Limitations

- Radiation exposure and safety tips
| Risk | How It Is Managed | Who Is Most Concerned |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation Exposure | Technologists use the lowest possible dose. Scans are only performed when medically necessary. Modern machines are designed to use less radiation. | Children and young adults are more sensitive to radiation. Patients requiring multiple scans over their lifetime. |
| Allergic Reaction to Contrast | You will be asked about allergies before the scan. Medical staff are trained to handle reactions immediately. | People with a history of allergies, especially to iodine or previous contrast dye. Patients with severe asthma. |
| Kidney Issues from Contrast | Your kidney function may be checked with a blood test before the scan. You'll be advised to drink plenty of water after the scan. | People with pre-existing kidney disease or diabetes. The elderly. |
- Allergic reactions to contrast dye
- Not suitable for pregnancy in most cases
Frequently asked questions
You lie on a flat bed that slowly moves through the centre of a large, ring-shaped machine. As you move, an X-ray scanner rotates around you, taking pictures from different angles. A computer then processes these pictures to create detailed cross-sectional images.
Doctors use CT scans to find and diagnose many medical problems quickly. This includes detecting internal injuries after an accident, locating tumours or infections, and finding blood clots or internal bleeding. It helps them see inside the head, chest, and stomach.
There is no fixed limit, but doctors only recommend a CT scan when it is truly necessary. This is because each scan exposes you to a small amount of radiation. The decision is always based on whether the benefit of the diagnosis is greater than the small risk.
The cost of a CT scan in India can vary widely, from around ₹1,500 to ₹15,000. The price depends on the city, the hospital, the part of the body being scanned, and whether a special contrast dye is needed for a clearer picture.
CT scans are generally very safe and are a common medical procedure. They use a small dose of radiation, and the benefit of finding a health problem usually outweighs this tiny risk. Some people may have a mild allergic reaction to the contrast dye if it is used.
The main benefits are that CT scans are fast, painless, and give extremely detailed images. They can show bones, muscles, organs, and blood vessels all in a single scan. This helps in making a quick and accurate diagnosis, especially in emergencies.
The main risk from repeated scans is the increased exposure to radiation over your lifetime. While the risk from one scan is very small, many scans can slightly increase the lifetime chance of developing cancer. This is why they are only performed when medically required.
The actual scanning process is very fast, often completed in less than a minute. However, the entire appointment, which includes preparation and positioning you on the machine, usually takes about 15 to 30 minutes from start to finish.

Dr. Swati Shah
MS, DrNB (Surgical Oncology)
Dr. Swati Shah is a renowned Robotic Uro and Gynecological Cancer Surgeon from Ahmedabad. He has 15+ years of extensive experience in pelvic oncosurgery and 10+ years of experience in robotic surgery. She treats cancers of kidney, bladder, prostate, uterus, ovaries and other pelvic organs.

